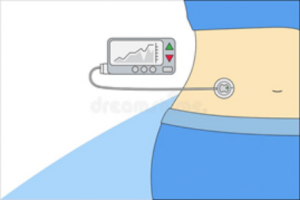
What is an Insulin Pump?
Insulin pumps are attached to the wearer twenty for hours a day (although can be disconnected for such activities as swimming, showering and intense physical activity if the person so desires). It is generally accepted a person should not disconnect from their pump for more than two hours at a time without reconnecting and at least checking blood glucose levels.
The pump is worn on the outside of the body. Individuals also sleep with their pump either in a pyjama pocket or simply in the bed with them!
Components of an Insulin Pump System
1 Reservoir – this sits inside the insulin pump and holds insulin. It needs to be changed every 2-3 days depending on the system used. All insulin pumps have alarms that will detect when the reservoir is low in insulin and let the wearer know that It must be changed.
Each insulin pump brand has their own reservoir that is specific to their pump.
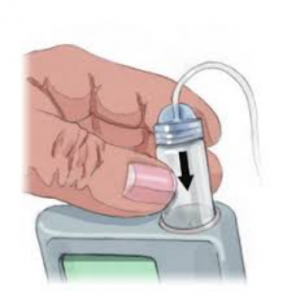
2 Infusion set or giving set -This is what attaches the reservoir in the insulin pump to the person with diabetes. The infusion set has a fine needle or cannula that is inserted just underneath the skin and needs to be replaced every two to three days.
In certain circumstances, people who have been diagnosed with ‘other diabetes’ and ‘hard to manage’ type 2 diabetes can request special consideration from the Department of Health to access IPCs (insulin pump consumables) through the NDSS.
Insulin pumps are generally covered under the top tier of private health. The IPP (Federal Government Insulin Pump Program), administered by JDRF, provides insulin pumps to low income families who have children (under 18 years of age) with type 1 diabetes. Although limited numbers, it does provide the opportunity for some children to gain access to pump therapy.
Components of an Insulin Pump System
Insulin pump therapy only uses short acting insulin. Research has shown that this type of diabetes management can reduce the frequency of severe hypoglycaemia (low blood glucose levels) and improve quality of life (QoL). Pump therapy may also help individuals manage their elevated glucose levels by improving their time in range and reducing fluctuations in the glucose levels.
Which pump to choose?
The model of insulin pump is up to the wearer and will depend on both the features and what each individual is looking to achieve. It may also be choice dependent on whether the pump has the capacity to connect with continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) which allows a small sensor the person is wearing to send a glucose reading to the pump every five minutes in real time. These decisions are made with the person with diabetes, the health care team, and the endocrinologist collectively.
Insulin Pump Companies
AMSL (Australasian Medical and Scientific Ltd)
Managing Diabetes
Medtronic
Roche Diabetes Care
Ypsomed
